
An ancient jawbone has been found on the ocean floor in Taiwan, and it seemingly details new information about a group of long-lost humans.
Learning about human ancestors is always interesting as it often provides intriguing details on how the planet was so many years ago.
And while you'd think we would know everything there is to know regarding our planet nowadays, scientists often find incredible finds on the planet we call home.
In Taiwan, experts have uncovered an ancient jawbone from the Penghu Channel which they say belongs to a group of early human relatives, who scientists only learnt last year were amongst those who humans were more than happy to jump into bed with.
Advert
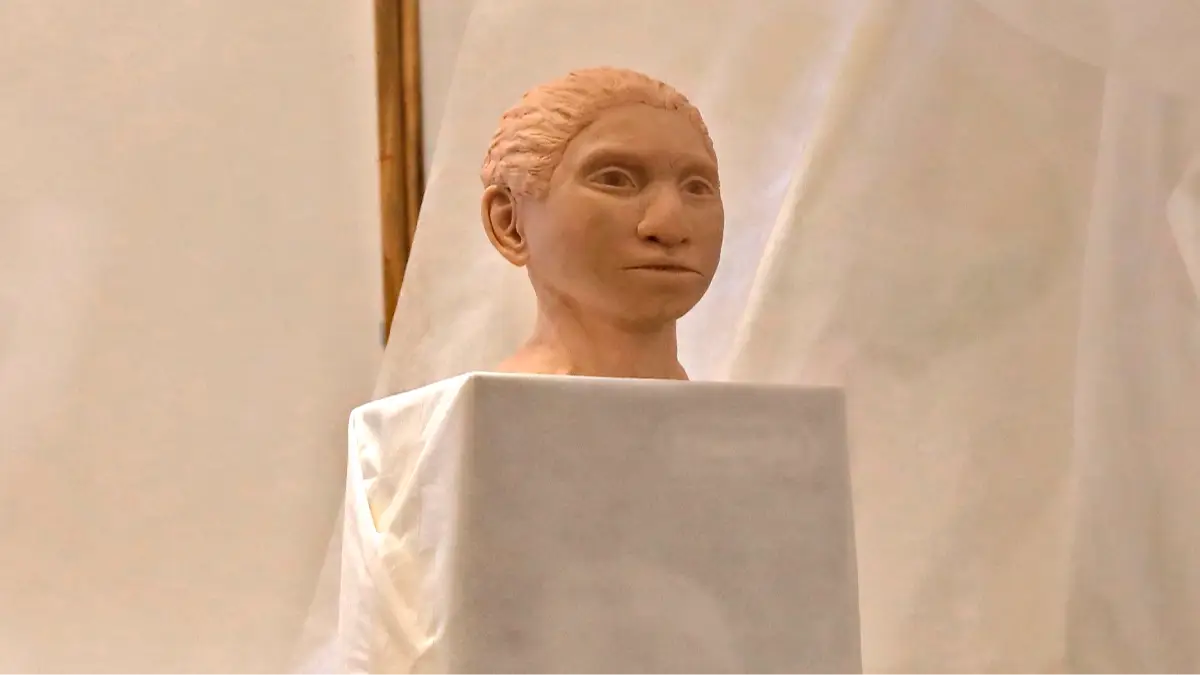
I guess that explains how this ancient child had parents of two different species.
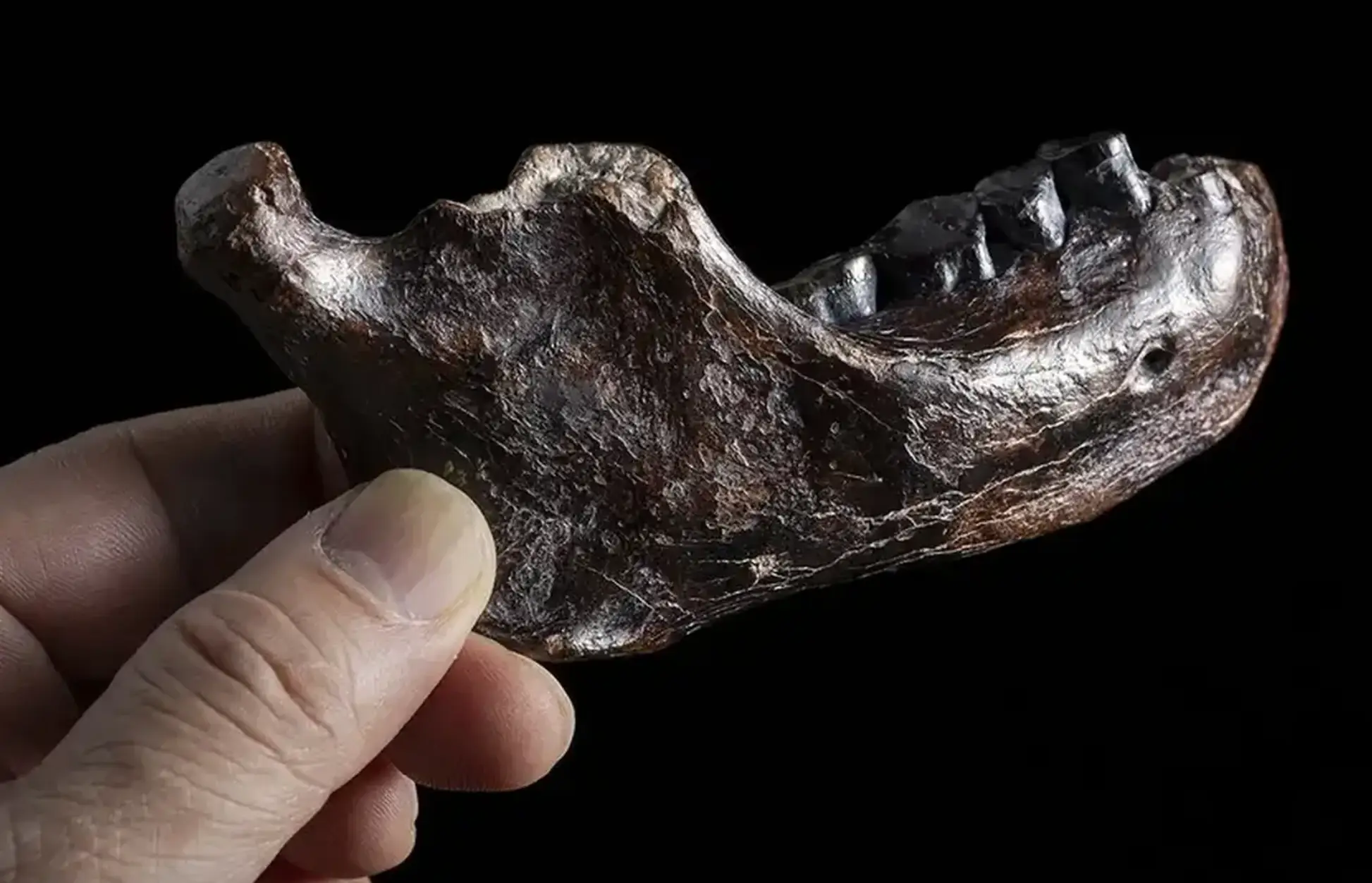
The 'very scarce' Denisovans, who co-existed with Neanderthals and Homo sapiens, remain a poorly understood group to this day, however, more is being found about this group.
According to The Independent, Denisovan fossils are limited to fragmented remains such as jawbones, teeth, and even a finger bone - so this recent discovery is certainly an interesting one.
After making an initial discovery when someone brought in the jawbone for further verification, scientists in Taiwan, Japan and Denmark were able to extract some protein sequences from a previously discovered incomplete jawbone, which was found to have belonged to a Denisovan man.
Frido Welker, an associate professor of biomolecular paleoanthropology at the University of Copenhagen in Denmark and co-author of the study, said (via CNN): "We’ve determined and shown over the past couple of years that these proteins can survive longer than DNA does, and that if we have decent recovery, we can say something about the evolutionary ancestry of a specimen."
And experts have since found protein sequences of the find also resemble that of a Denisovan fossil that was initially recovered in Siberia.
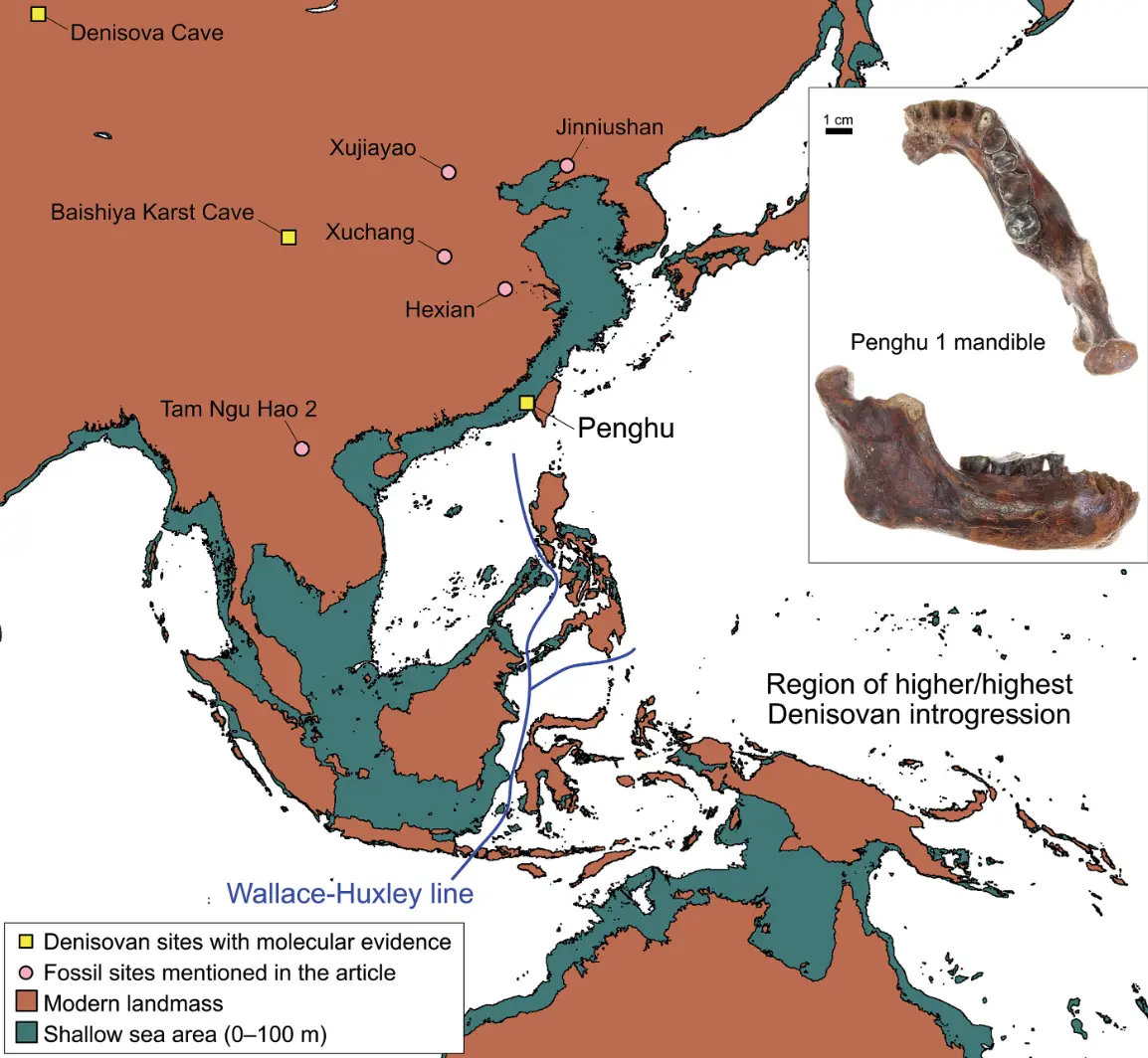
Zhang Dongju, a archaeologist and professor at Lanzhou University in China, said: "With the accumulation of Denisovan fossils and the increase of Denisovan-specific molecular signature identified, identification of Denisovan fossils will be easier.
"And I believe more Denisovan fossils will be found and identified in [the] future. And we will know more about this mysterious species."
While the latest find is certainly a huge development, experts are warning a lot of mystery still surrounds the discovery and that more research and studies are required to help uncover the full truth.
Ryan McRae, a paleoanthropologist at the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History, said to CNN: "Neither mandible has a chin, like modern humans do, so the front of their jawline would probably look flatter than ours.
"The authors wisely point out that the Penghu mandible is male, which means that it may exhibit the larger, more robust end of variation for this species. In other words, female Denisovans could look the same, or quite different, we just don’t know yet."
The full findings can be found in the journal Science.
Topics: Science
