
A solar storm alert has been issued for Earth after an eruption on the sun.
A number of strong geomagnetic storms have been observed in recent hours, according to the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
This comes after intense activity on the sun caused two different 'filament eruptions' – also known as coronal mass ejections – which released powerful, magnetised solar winds towards our planet.
The NOAA has ranked the storm as G3, which is classified as strong. The worst-case scenario of such a storm could see issues with satellites and humans currently in space, as well as interference with radio and navigation systems, and disruption to migratory animals.
On the more harmless side of the spectrum, solar storms can also cause extraordinary sights like the Northern Lights, which were seen during the latest spike.
Advert
A geomagnetic storm is a "major disturbance of Earth's magnetosphere that occurs when there is a very efficient exchange of energy from the solar wind into the space environment surrounding Earth," the NOAA said.
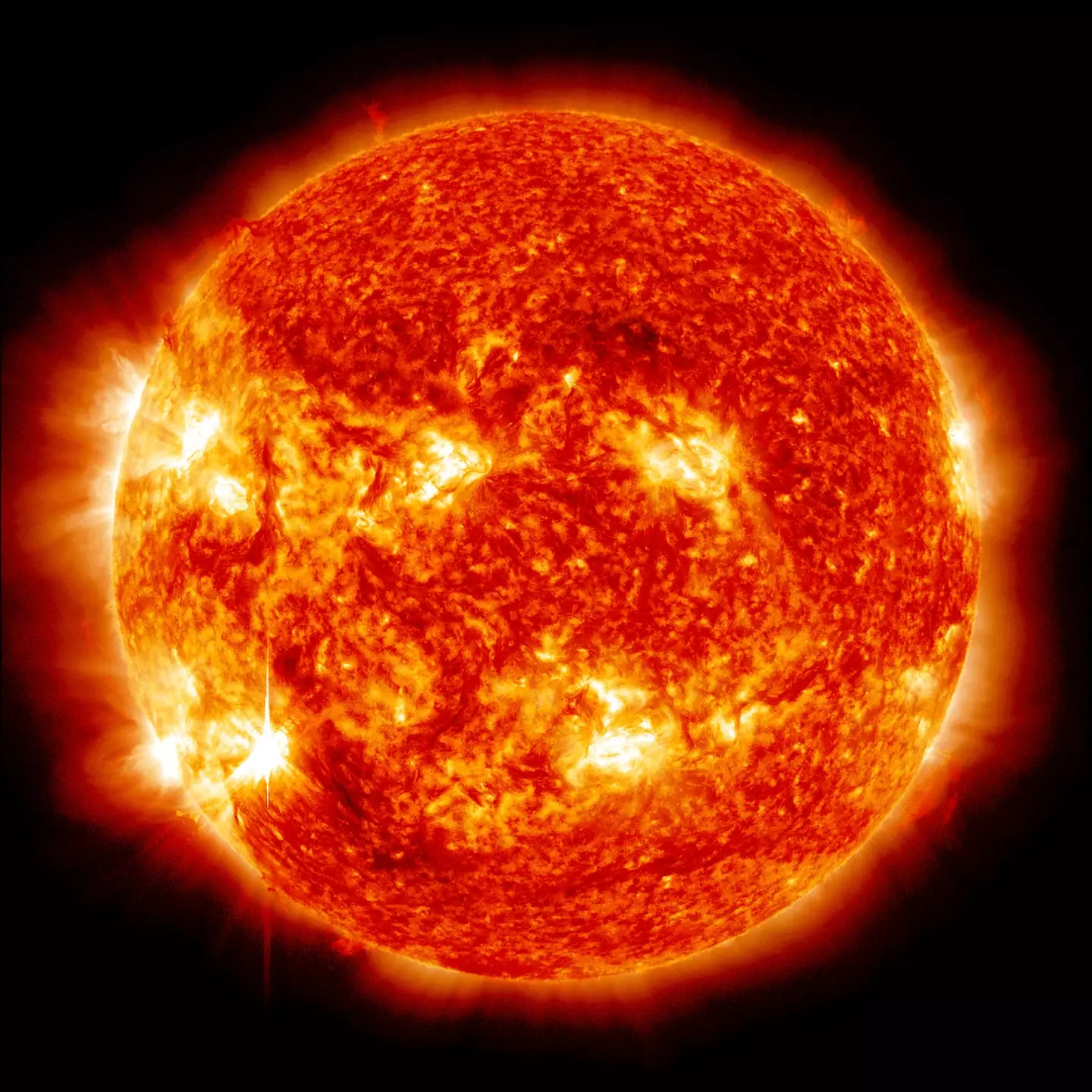
"These storms result from variations in the solar wind that produces major changes in the currents, plasmas, and fields in Earth’s magnetosphere," it added.
For reference, in the event of a G5 storm, we could see a "radio blackout on the entire sunlit side of the Earth lasting for a number of hours. This results in no HF radio contact with mariners and en route aviators in this sector."
This storm was also predicted by Space Weather, which detailed how a 'dark filament of magnetism just whipsawed out of the sun's atmosphere, carving a gigantic canyon of fire', the walls of which were estimated to be at least 20,000km high.
Dr. Tony Phillips, who runs Space Weather, said: "Magnetic filaments are plasma-filled tubes of magnetism that meander through the sun’s atmosphere. They easily become unstable and erupt, hurling fragments of themselves into space."
These storms have affected Earth before, most notably in 1859, known as the 'Carrington Event'.
It was the largest geomagnetic storm on record, causing bright aurora across the planet and damaging the fairly limited electrical and communication lines in place at that time.
Also earlier this year, Elon Musk's Starlink project was impacted by a geomagnetic storm when 40 of its 49 satellites were destroyed. They were planned to provide constant internet coverage for most of the world.
If you have a story you want to tell, send it to UNILAD via [email protected]